
Key Takeaways
- Chain abstraction addresses blockchain fragmentation by enabling seamless communication and transactions across diverse networks.
- Cross-chain communication protocols like LayerZero and Chainlink CCIP facilitate secure message passing between blockchains.
- Account aggregation simplifies user experiences by allowing single-account access across multiple chains, as seen in NEAR’s approach.
- Universal frameworks like the Omnichain Web integrate multiple chain abstraction methods for scalable, AI-driven blockchain ecosystems.
- Chain abstraction powers advanced DeFi protocols and real-time applications, but security and decentralization challenges remain.
Chain abstraction represents a transformative approach to solving interoperability challenges across blockchain networks, enabling seamless communication and transactions between previously isolated chains. As blockchain ecosystems proliferate, with each network developing unique capabilities and limitations, chain abstraction technologies provide the necessary infrastructure to unify these fragmented systems. This Innovation and Tech report examines the core concepts, leading approaches, significant projects, and future implications of chain abstraction in cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Conceptual Foundations Of Chain Abstraction
Chain abstraction fundamentally addresses the fragmentation problem plaguing Web3 ecosystems. The blockchain landscape currently consists of siloed networks with distinct transaction formats, consensus mechanisms, and programming environments. This fragmentation hinders the mass adoption of blockchain technology and restricts the development of comprehensive decentralized applications. Chain abstraction creates higher-level interfaces that shield users and developers from underlying blockchain complexities, allowing them to interact with multiple chains through unified protocols.
The concept extends beyond simple cross-chain asset transfers, which represent only one application of chain abstraction. At its essence, chain abstraction encompasses three interconnected capabilities: cross-chain communication (message passing between blockchains), unified account management (controlling multiple chain identities through a single interface), and cross-chain execution (running operations that span multiple blockchains atomically). These capabilities collectively enable a more cohesive and accessible blockchain ecosystem that can compete with the seamless user experiences available in traditional Web2 applications.
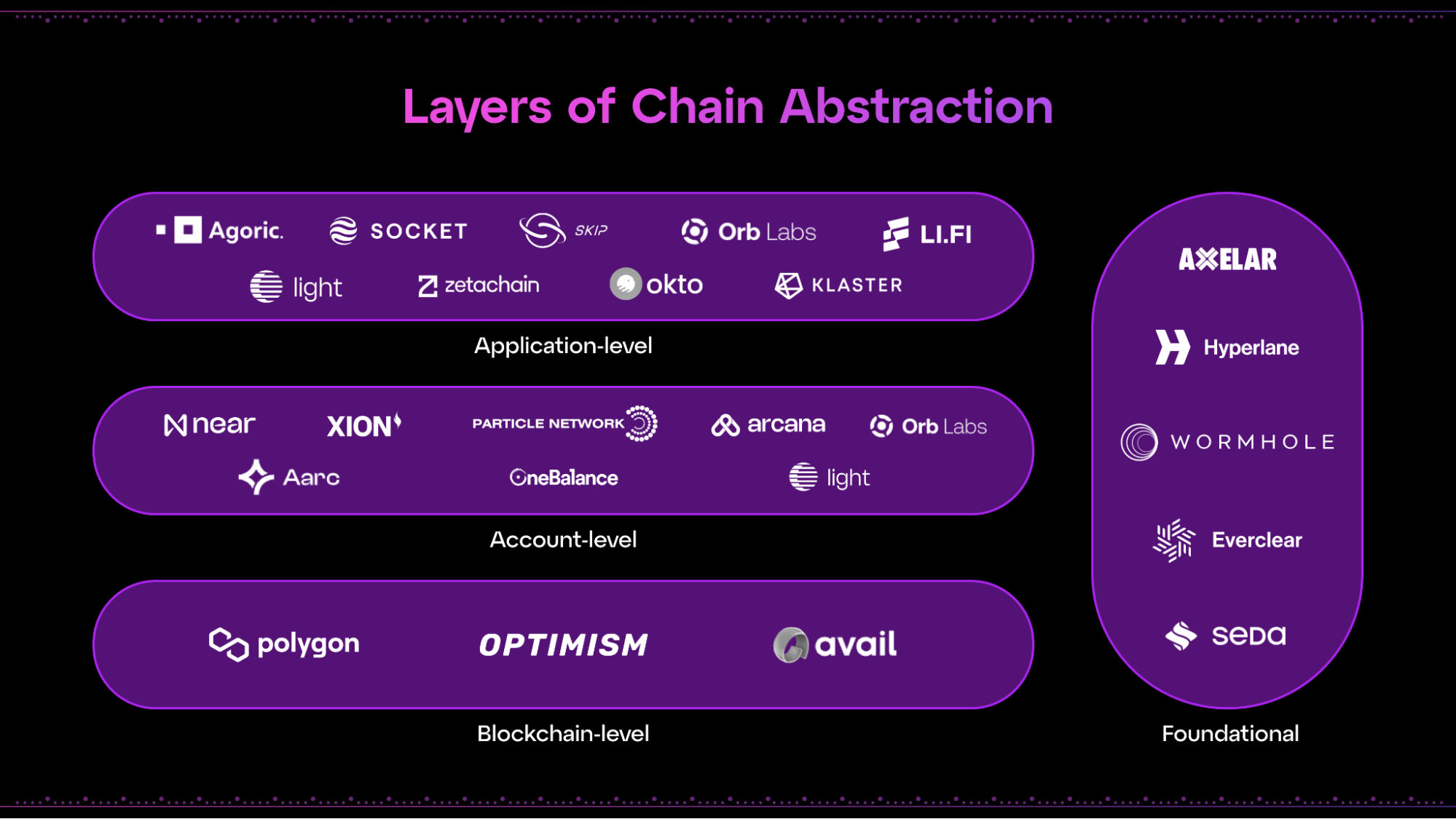
Major Approaches To Chain Abstraction
Cross-Chain Communication Protocols
Cross-chain communication protocols form the foundation of many chain abstraction solutions. These protocols facilitate message passing between different blockchains, enabling information exchange and coordinated actions across network boundaries. LayerZero exemplifies this approach, providing lightweight message transmission between chains through a specialized architecture incorporating oracles and relayers. LayerZero deploys “LayerZero Endpoints” on each supported chain, which function as lightweight clients that communicate between blockchains. This design separates the intermediate trust link into two components, lowering fees while maintaining security.
Similarly, Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) enables developers to build applications that transfer tokens, messages, or both across chains. CCIP emphasizes security through defense-in-depth mechanisms, including multiple independent nodes run by separate key holders and three decentralized networks that verify every cross-chain transaction. These protocols create the communication infrastructure necessary for more complex chain abstraction solutions.
Account Aggregation Methods
Account aggregation represents another approach to chain abstraction, focusing on simplifying user experiences through unified key management. NEAR’s implementation exemplifies this strategy, allowing users to sign and transact on multiple blockchains using a single NEAR account. This method eliminates the need to create separate accounts with distinct key pairs for each blockchain. NEAR even supports linking OpenID Connect accounts to blockchain identities, enabling users to access multiple chains through familiar authentication methods like email login.
The account aggregation approach directly addresses one of the most significant barriers to blockchain adoption: complex key management. By centralizing identity across chains, users can navigate the multichain ecosystem without managing numerous wallets and seed phrases, bringing the user experience closer to Web2 standards while maintaining the security benefits of blockchain technology.
Universal Frameworks
Universal frameworks provide comprehensive solutions that combine multiple chain abstraction methods into cohesive systems. The Omnichain Web represents an ambitious example, introducing a framework that bridges Web2, Web3, and AI technologies. This framework incorporates several components, including OmniRollups for scalable cross-chain execution, an Omni Sequencer for atomic transaction processing, and Linera microchains for AI-driven automation. Such frameworks move beyond addressing specific interoperability challenges to reimagine the entire blockchain infrastructure as an integrated system.
Leading Projects Implementing Chain Abstraction
Three major projects currently dominate the chain abstraction landscape: Axelar, Wormhole, and LayerZero. Each employs distinct approaches to enable cross-chain interoperability.
Axelar Network functions as a Layer 1 blockchain dedicated to cross-chain interoperability, connecting over 60 blockchains through Gateway smart contracts that link the Axelar network to external chains. This infrastructure supports not only information and asset bridging but also the execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications across networks. Axelar’s validator network runs a cross-chain gateway protocol that sits atop connected blockchains, enabling consensus-driven cross-chain transactions.
LayerZero focuses exclusively on message transmission between blockchains, deliberately avoiding asset transfers to maintain a clear focus. Its ultra-light node (ULN) architecture divides trust between relays and oracles, optimizing for efficiency and security. LayerZero supports any blockchain capable of running smart contracts, including non-EVM chains like Aptos.

Chain Abstraction Applications & Use Cases
Chain abstraction technologies enable numerous applications that were previously impractical in fragmented blockchain environments:
- Cross-chain decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols that access liquidity and functionality across multiple blockchains
- Simplified user experiences with single account login across blockchain ecosystems
Chain abstraction also enables entirely new categories of applications through higher performance and lower latency. Projects like MegaETH aim to deliver real-time blockchain performance with throughput exceeding 100,000 transactions per second and sub-millisecond latency2. Such performance characteristics could attract high-frequency trading applications and complex DeFi protocols to Ethereum Layer 2 solutions, expanding the market for blockchain applications.
Challenges & Future Outlook
Despite its promise, chain abstraction faces significant challenges. Security represents the primary concern, as cross-chain transactions introduce new attack vectors and trust assumptions. Different approaches make varying trade-offs between security, decentralization, and performance. LayerZero’s reliance on oracles and relayers introduces specific trust assumptions, while projects like MegaETH use single-sequencer models that enhance speed at the cost of greater centralization.
The future likely involves increased standardization around successful protocols and frameworks, similar to how TCP/IP emerged as the standard for internet communication. Research on atomic multi-chain transactions and formal verification methods for cross-blockchain interactions will advance the security and reliability of chain abstraction solutions. Additionally, the emergence of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) may introduce new requirements for interoperability with traditional financial systems, further driving chain abstraction development.
Unifying Blockchain Ecosystems For Seamless Interoperability
Chain abstraction represents a crucial evolution in blockchain technology, addressing fundamental interoperability challenges that have limited widespread adoption. By enabling seamless communication between blockchains, simplifying account management, and facilitating cross-chain applications, chain abstraction technologies create a more accessible and powerful blockchain ecosystem. As these technologies mature, they will likely accelerate the integration of blockchain capabilities into mainstream applications and financial systems, potentially realizing the transformative potential of decentralized technologies beyond current cryptocurrency use cases.






