Key Takeaways
- Crypto ETFs provide regulated, accessible exposure to cryptocurrencies, simplifying investment for retail and institutional investors.
- Spot ETFs track cryptocurrency prices directly by holding actual assets, while futures ETFs use contracts, impacting tracking accuracy.
- The SEC’s 2024 approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs marked a pivotal shift, enhancing cryptocurrency legitimacy and market integration.
- Crypto ETFs influence market volatility and offer portfolio diversification, with varying benefits based on investor risk profiles.
- Ongoing regulatory evolution and tracking efficiency are critical areas for future Crypto ETF development and adoption.
Crypto ETFs, or Cryptocurrency Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), represent one of the most significant developments in the integration of digital assets into traditional financial markets. These investment vehicles provide regulated exposure to cryptocurrencies for mainstream investors without the complexities of direct ownership. The January 2024 approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission marked a watershed moment in cryptocurrency legitimization, ending years of regulatory reluctance and opening new avenues for institutional and retail investor participation. As these financial instruments continue to evolve, they serve as critical bridges between conventional finance and the emerging digital asset ecosystem.
The cryptocurrency market has historically presented significant barriers to entry for traditional investors, including custody challenges, security concerns, and technical complexity. Crypto ETFs address these issues by offering familiar investment structures that operate within established regulatory frameworks, trading on conventional exchanges during standard market hours. This accessibility has attracted both individual investors seeking simplified exposure to digital assets and institutional players looking to diversify their portfolios without navigating the intricacies of cryptocurrency exchanges.
This Innovation and Tech report explores the developments, inner workings, mechanisms, and landscape for Crypto ETFs.
Types Of Crypto ETFs
Crypto ETFs primarily exist in two distinct forms: spot ETFs and futures ETFs, each with unique structures and implications for investors. Spot Bitcoin ETFs directly own the underlying cryptocurrency, purchasing and storing actual bitcoins as the fund’s primary assets. This direct ownership enables these funds to closely track Bitcoin’s price movements, with performance that mirrors the cryptocurrency’s fluctuations minus management fees. The structure provides investors with exposure that closely approximates direct ownership while eliminating the need to manage private keys or navigate cryptocurrency exchanges.
Futures-based crypto ETFs, which preceded spot offerings in many markets, operate differently by holding futures contracts rather than the underlying digital assets. These contracts represent agreements to buy or sell cryptocurrency at predetermined future dates and prices. While this approach allows investors to gain exposure to cryptocurrency price movements, it often results in less precise tracking compared to spot ETFs due to factors such as contango, backwardation, and roll costs that affect futures markets. These discrepancies can create meaningful performance divergences between futures ETFs and the actual cryptocurrency prices they attempt to track.
The operational differences between these ETF types extend beyond performance tracking to include risk profiles and regulatory considerations. Spot ETFs face challenges related to cryptocurrency custody, security protocols, and valuation methodologies, while futures ETFs confront risks associated with derivatives markets, including potential liquidity constraints and heightened volatility. Both structures represent significant advances in cryptocurrency accessibility, though they cater to different investor preferences regarding exposure directness, tracking accuracy, and risk tolerance.
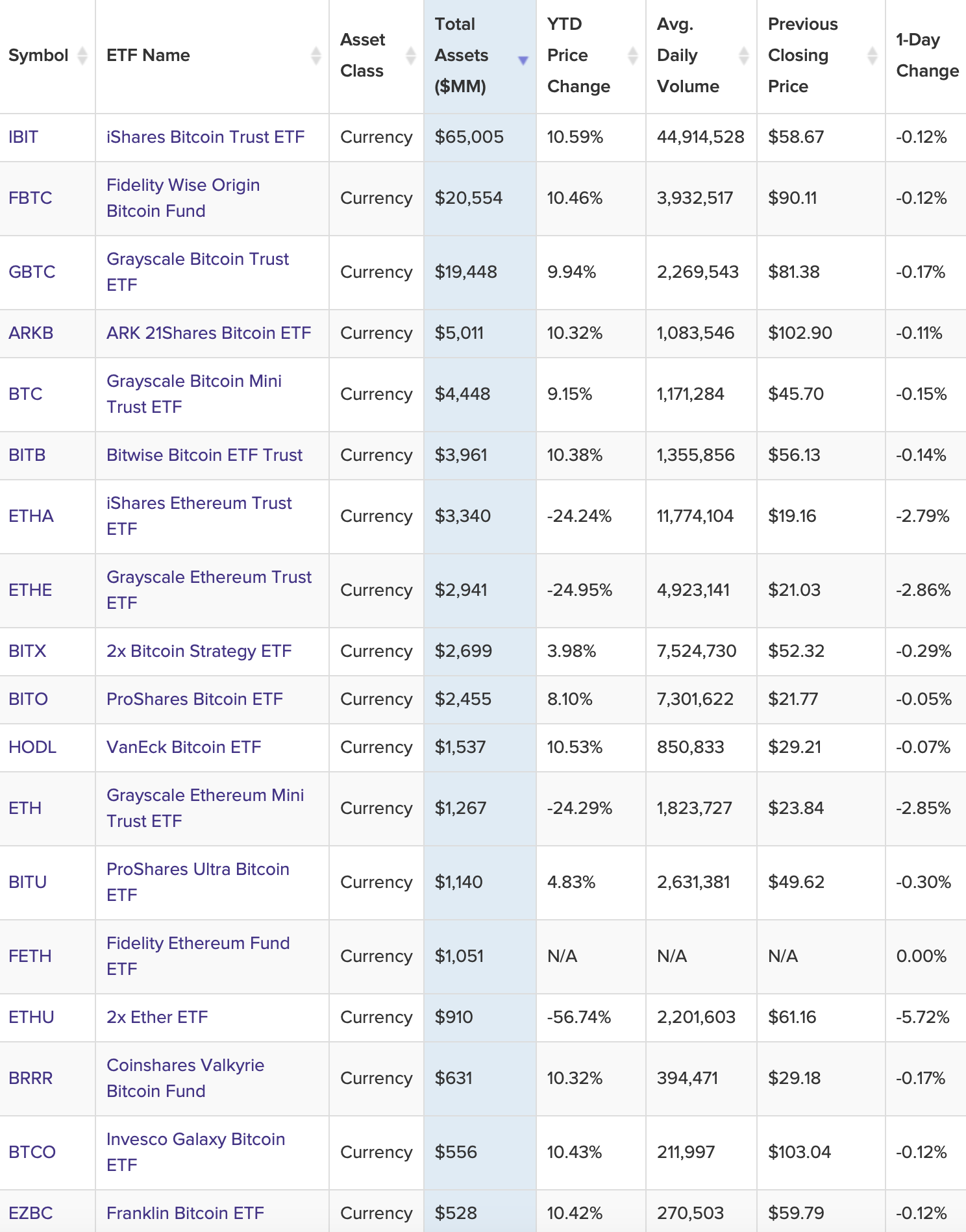
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory journey of crypto ETFs demonstrates the evolving relationship between traditional financial regulations and digital asset innovations. Before January 2024, U.S. regulators consistently rejected spot Bitcoin ETF applications, citing concerns about market manipulation, custody security, and investor protection. This stance created a regulatory divergence between the United States and several other jurisdictions where spot crypto ETFs had already gained approval. The SEC’s eventual approval of multiple spot Bitcoin ETFs represented a significant reversal and recognition of the maturing cryptocurrency market infrastructure.
Global regulatory approaches to crypto ETFs vary considerably, reflecting differing perspectives on digital assets across jurisdictions. Some countries embraced these investment vehicles earlier, while others maintain restrictive postures or are still developing appropriate frameworks. These regulatory differences influence market development and investor access, creating a patchwork of availability that compounds the already complex cryptocurrency investment landscape. As regulations continue to evolve, market participants must navigate these differences while anticipating future regulatory developments that could significantly impact crypto ETF operations and accessibility.
How Crypto ETFs Shape Volatility & Portfolio Diversification
The introduction of crypto ETFs has measurably affected both cryptocurrency and traditional markets, creating new dynamics and relationships between these previously distinct domains. Research indicates significant bidirectional volatility spillovers between cryptocurrencies and traditional financial assets, with Bitcoin acting as a major transmitter of market volatility. This interconnection demonstrates how crypto ETFs contribute to market integration while potentially transferring cryptocurrency volatility into conventional financial systems.
Crypto ETFs offer several advantages for portfolio construction and risk management. Including cryptocurrencies in traditional portfolios potentially provides diversification benefits, though these vary based on investor preferences and allocation frequencies. Research suggests different investor types—whether risk-averse, return-seeking, or diversification-preferring—may achieve utility gains by incorporating cryptocurrencies into their asset allocations. This utility derives from cryptocurrencies’ distinct statistical parameters and correlation profiles compared to established asset classes.
The investment case for crypto ETFs extends beyond simple exposure to include considerations about underlying cryptocurrency fundamentals, market dynamics, and evolving use cases. Institutional investors increasingly differentiate between various cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin often viewed as a “digital gold” store-of-value asset. This differentiation highlights the importance of understanding the distinct properties and market positioning of cryptocurrencies underlying various ETFs. The segmentation between core and satellite cryptocurrencies further suggests differentiated approaches to investment allocation strategies.
Performance tracking represents a critical consideration for crypto ETF investors, particularly when comparing spot versus futures-based offerings. Spot ETFs typically achieve more precise price performance relative to their underlying assets, functioning similarly to physically-backed commodity ETFs. This tracking accuracy comes with trade-offs, including limited trading hours compared to the 24/7 cryptocurrency markets and exposure to custody risks. Investors must weigh these factors against the regulated accessibility and simplified tax treatment that crypto ETFs provide.
Crypto ETFs: Pioneering Institutional Access To Digital Assets
Crypto ETFs represent a significant evolutionary step in the financial ecosystem’s adaptation to digital assets. By providing regulated, accessible investment vehicles, these products facilitate broader market participation while potentially accelerating institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies. The continued development of the crypto ETF landscape, including recent approvals of Bitcoin ETF options and potential future expansion to other digital assets, suggests growing integration between traditional and crypto financial systems.
The future research agenda for crypto ETFs should address several critical areas, including long-term tracking efficiency, regulatory evolution across different jurisdictions, and the impact on cryptocurrency market structures and price discovery mechanisms. As these investment vehicles mature, they will likely influence cryptocurrency adoption trajectories, market liquidity, and volatility patterns. Whether crypto ETFs ultimately serve as transitional vehicles toward broader cryptocurrency adoption or become the preferred access point for most investors remains an open question with significant implications for both the cryptocurrency ecosystem and traditional financial markets.