
Key Takeaways
- Decentralized Identity empowers users to control their digital identities without relying on centralized authorities.
- Blockchain-based solutions like DIDs and verifiable credentials ensure secure, user-centric identity management.
- Zero-knowledge proofs and selective disclosure enhance privacy in Decentralized Identity verification processes.
- Platforms like Hyperledger Indy provide robust infrastructure for Decentralized Identity networks.
- Challenges such as interoperability and trust establishment remain critical for widespread Decentralized Identity adoption.
Decentralized identity represents a paradigm shift from traditional centralized identity management systems toward user-controlled, blockchain-based solutions that fundamentally enhance privacy and security. Current research demonstrates that decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and self-sovereign identity (SSI) frameworks enable individuals to maintain complete control over their digital identities without relying on centralized authorities, while cryptographic mechanisms like zero-knowledge proofs provide unprecedented privacy protection during identity verification processes.
This Innovation and Tech article explores how Decentralized Identity is reshaping digital trust through blockchain-based identifiers, verifiable credentials, and zero-knowledge cryptography—empowering individuals with full control over their personal data while advancing privacy, security, and user autonomy across digital ecosystems.
Evolution From Centralized To Decentralized Identity Models
Traditional digital identity systems suffer from inherent vulnerabilities stemming from their centralized architecture, where trusted authorities and third-party operators control user data and verification processes. These systems create single points of failure, expose users to data breaches, and enable tracking across multiple platforms through correlation of identifiers like social security numbers or usernames. The centralized model fundamentally conflicts with user privacy and autonomy, as individuals lack meaningful control over their personal information.
Self-sovereign identity emerges as the next evolution of identity management models, positioning users at the center of the identity ecosystem. Unlike federated identity systems that merely distribute trust among multiple authorities, SSI empowers individuals to maintain and control their data directly. When service providers request user information, individuals can transmit data directly without intermediary involvement, fundamentally altering the power dynamics of digital identity. This shift fosters greater societal trust by prioritizing individual autonomy and reducing reliance on opaque institutional frameworks.
The transition to decentralized identity leverages distributed ledger technology to eliminate dependence on centralized registries and certificate authorities. This architectural shift enables the creation of verifiable, self-sovereign digital identities that remain fully under user control while maintaining cryptographic integrity and authenticity.

Technical Foundations Of Decentralized Identity Infrastructure
Decentralized identifiers serve as the foundational building blocks of blockchain-based identity systems, functioning as globally unique identifiers that require no centralized registration authority. DIDs are URIs that associate subjects with DID documents, enabling trustable interactions through cryptographic material and verification methods. The W3C specification establishes that DIDs can refer to any subject, persons, organizations, things, or abstract entities, as determined by the DID controller. Their compatibility with various blockchain networks ensures scalability across diverse ecosystems.
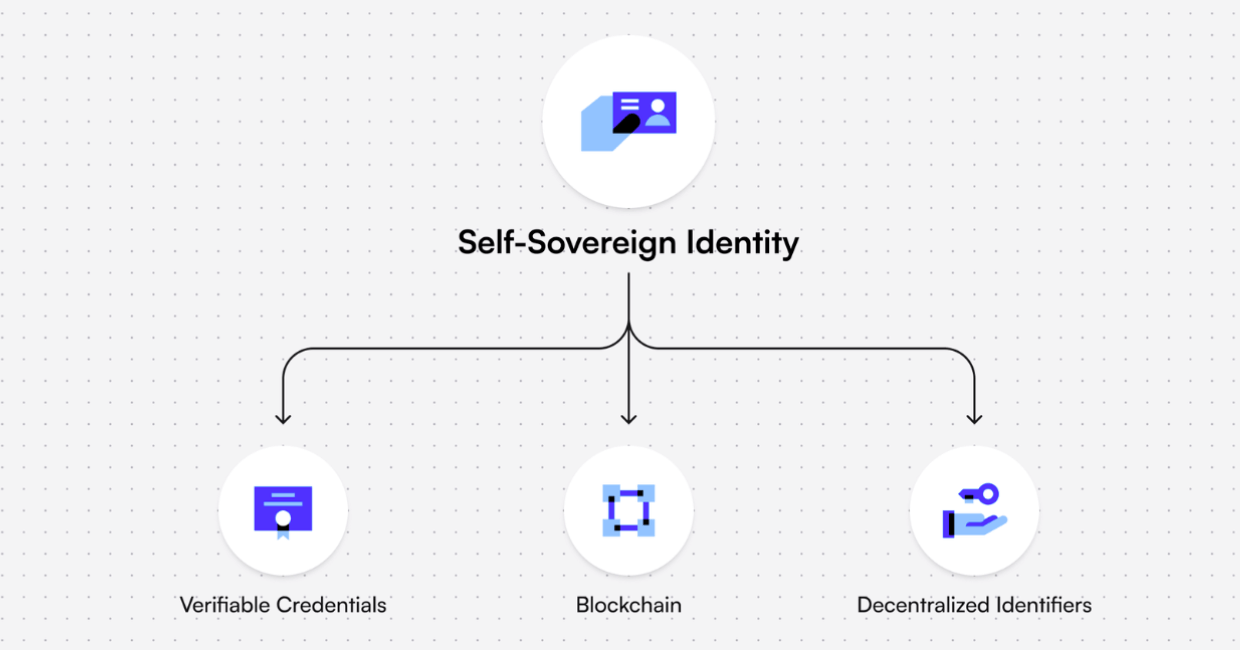
The technical architecture incorporates verifiable credentials as digitally signed attestations that enable identity holders to prove specific claims about themselves. These credentials contain metadata cryptographically signed by issuers, establishing properties such as expiry dates, verification keys, and revocation mechanisms. The separation of credential issuance from verification creates a flexible ecosystem where users can selectively disclose information without revealing unnecessary personal data.
Distributed ledger technology provides the infrastructure for maintaining decentralized identity networks without centralized control points. Blockchain networks like Hyperledger Indy implement public permissioned ledgers specifically designed for identity management, utilizing consensus mechanisms such as the Plenum protocol to validate transactions and maintain network integrity. This infrastructure enables multiple independent identities per user, each with distinct public-private key pairs, providing granular control over different aspects of digital identity.
Privacy & Security Mechanisms In Decentralized Systems
Zero-knowledge proofs represent a critical advancement in privacy-preserving identity verification, enabling entities to prove knowledge of specific information without disclosing the underlying data. These cryptographic techniques allow identity holders to demonstrate compliance with requirements: such as age verification or credential validity, while maintaining complete privacy over actual values. For instance, users can prove they meet minimum height requirements without revealing their exact measurements, preserving privacy while satisfying verification needs. Ongoing cryptographic advancements continue to enhance the scalability of these privacy-preserving mechanisms across large-scale identity networks.
Selective disclosure mechanisms further enhance privacy protection by allowing credential holders to reveal only necessary information during verification processes. Zero-knowledge selective disclosure verifiable credentials (ZK-SD-VCs) grant holders total control over which credential portions remain concealed from verifiers. This capability contrasts with alternative approaches where issuers predetermine which fields can be concealed, placing privacy control directly in user hands.
The implementation of pairwise pseudonymous identifiers significantly reduces correlation risks that plague traditional identity systems. Sovrin’s approach separates data from direct identifiers, preventing linkage to identity without additional separately-held information. This design creates compartmentalized identity relationships where interactions with different services utilize distinct identifiers, eliminating the tracking capabilities that characterize centralized systems.
Biometric authentication integration through protocols like BioZero demonstrates advanced privacy-preserving approaches to decentralized identity verification. These systems enable direct biometric authentication on blockchain networks while maintaining privacy through cryptographic protection of biometric templates. Such implementations address Sybil attack vulnerabilities while preserving the privacy advantages of decentralized architectures.
Implementation Approaches & Platform Architectures
Hyperledger Indy exemplifies sophisticated implementation of decentralized identity infrastructure through its four-component architecture comprising identity providers, independent identities, validators, and users. The platform eliminates centralized identity providers while maintaining standardized frameworks for creating, sharing, and revoking identities. Validator nodes operate consensus protocols to validate transactions in distributed fashion, while users can verify identities directly through public ledger access.
Contemporary research proposes novel approaches like ZKBID that address endemic mistrust in blockchain account systems by linking blockchain accounts to humans in one-to-one mappings. These systems aim to reflect genuine social relationships and interactions between real users rather than anonymous blockchain addresses. Such implementations demonstrate evolution toward more sophisticated identity architectures that balance anonymity with accountability.
The UniqueID project represents another significant implementation approach, proposing a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) for maintaining human identities with strict one-person-one-ID properties. This approach extends blockchain decentralization beyond money and computation to human identity concepts, creating verified human identity lists through distributed consensus mechanisms. Its potential integration with existing identity frameworks enhances its applicability in real-world scenarios.
Decentralized Identity: Transforming Digital Trust & Privacy
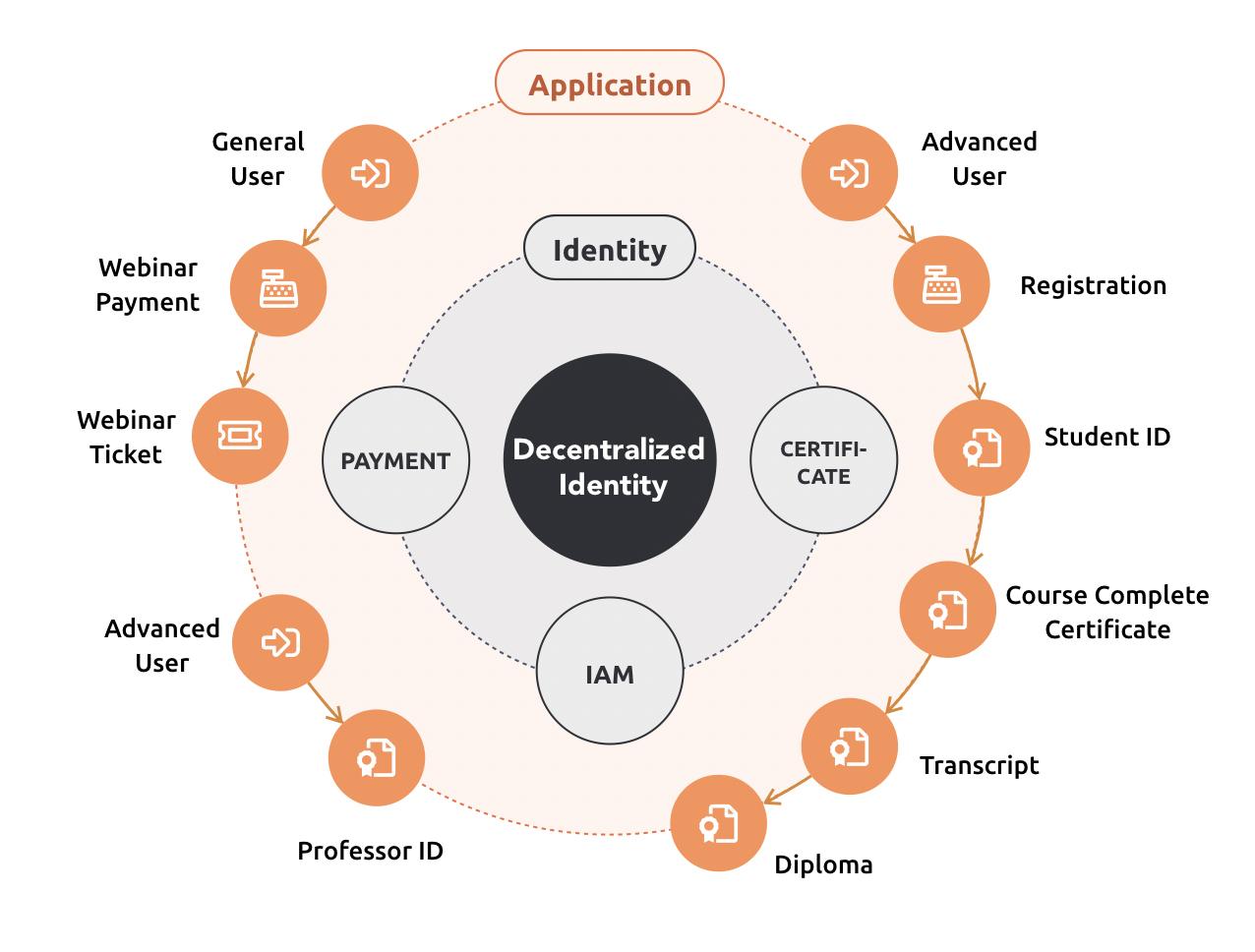
Decentralized identity represents a transformative approach to digital identity management that addresses fundamental privacy and security limitations of centralized systems through blockchain-based infrastructure and cryptographic innovation. The combination of decentralized identifiers, verifiable credentials, zero-knowledge proofs, and selective disclosure mechanisms creates unprecedented user control over personal data while maintaining verification integrity. These technological advances enable individuals to prove identity claims without unnecessary data exposure, fundamentally rebalancing power dynamics in digital interactions. As decentralized identity systems mature, their potential to redefine digital trust promises a future where privacy and autonomy are foundational to online interactions.
The continued evolution of decentralized identity platforms demonstrates significant potential for widespread adoption. As regulatory frameworks like the European Union’s EUDI Digital Identity initiative begin incorporating SSI principles, the transition toward user-controlled identity systems appears increasingly inevitable, promising enhanced privacy, security, and individual autonomy in digital environments.





