Key Takeaways
- DeFAI represents a new frontier in financial infrastructure where artificial intelligence and decentralized protocols combine to create intelligent, adaptive, and trust-minimized financial systems.
- These protocols leverage AI agents to automate trading strategies, risk management, asset allocation, and governance, offering a dynamic alternative to static DeFi primitives.
- Technological layers such as decentralized compute networks, AI inference modules, and verifiable machine learning (zkML) support the execution and trustworthiness of autonomous financial logic on-chain.
- Projects like Autonolas, Allora, Modulus, and Ritual are building modular infrastructure that enables DeFAI agents to act within DeFi environments, coordinating capital, optimizing yield, and reacting to real-time market conditions.
- DeFAI is not a single protocol but a movement toward composable, intelligent capital coordination systems that integrate learning, automation, and user-driven governance into the fabric of Web3 finance.
The growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) has transformed access to financial markets by eliminating intermediaries, enabling smart contract-based lending, trading, and staking platforms. However, most DeFi protocols operate as deterministic, rules-based systems. They rely on static logic, predefined incentives, and passive liquidity rather than active strategy. In parallel, artificial intelligence has surged to the forefront of technological innovation, with models capable of prediction, pattern recognition, and autonomous decision-making.
The emerging field of DeFAI, Decentralized Financial Artificial Intelligence, represents the convergence of these two paradigms. It seeks to create financial systems that are not only decentralized and trustless but also intelligent and adaptive. In contrast to traditional DeFi, where users must manually execute strategies and adjust for market dynamics, DeFAI envisions systems where autonomous agents learn, coordinate, and act in real-time across on-chain environments.
This Innovation and Tech report offers a comprehensive overview of the DeFAI model, examining its architecture, operational logic, use cases, technological dependencies, and future implications. It presents DeFAI not as a trend, but as a foundational shift in how finance, intelligence, and automation intersect on-chain.
What Is DeFAI? Defining A New Financial Paradigm
DeFAI refers to decentralized financial systems incorporating artificial intelligence as a core operating component. These systems move beyond programmable finance toward autonomous finance, where smart contracts are paired with AI models that can make predictions, optimize returns, adapt to volatility, and govern protocol behavior without centralized oversight.
Unlike traditional DeFi protocols that rely on user-initiated interaction, DeFAI agents proactively analyze data, adjust strategies, and coordinate across contracts and chains. These agents may perform tasks such as forecasting yield changes, rebalancing liquidity across pools, or dynamically adjusting loan parameters based on predicted borrower risk. The output of these models is verified on-chain or routed through decentralized oracle networks, ensuring transparency and auditability.
Fundamentally, DeFAI expands the functional frontier of DeFi from automation to autonomy. It envisions self-executing and self-optimizing protocols, blending blockchain’s trustlessness with the adaptability of machine learning.
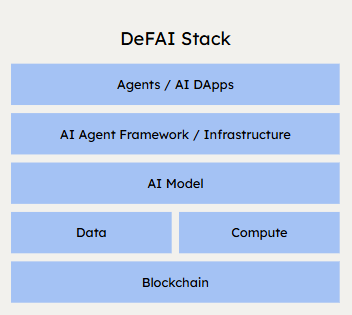
Technical Architecture of DeFAI Systems
The technical model of DeFAI systems integrates several interdependent layers, each designed to support decentralized intelligence within financial applications.
At the base layer is blockchain infrastructure, which provides the immutable ledger, programmable contracts, and token rails for executing financial logic. This includes existing DeFi platforms and execution environments such as Ethereum, Arbitrum, or Cosmos appchains.
Above this, DeFAI systems incorporate AI agent layers, software entities that observe, learn, and act within defined policy boundaries. These agents may be model-driven (trained on historical and real-time data) or rule-enhanced (operating with embedded thresholds or reinforcement incentives). Crucially, they interact directly with on-chain contracts to implement decisions, not via off-chain intermediaries.
The execution of these models requires decentralized compute networks (e.g., Bittensor, io.net, Gensyn), where inference workloads are distributed across node operators to prevent centralized control. Where required, zero-knowledge machine learning (zkML) can be applied to prove model outputs without revealing private data, thus ensuring verifiability.
Data feeds and feedback loops are essential for DeFAI. These are provided by oracles and data DAOs, which route information such as token prices, market sentiment, user behavior, or economic indicators to agents for continuous learning. Protocols like Modulus and Ritual are experimenting with on-chain model registries and signal aggregators to optimize agent training.
Finally, a governance and staking layer typically supports the economic alignment of agent behavior, using token-based voting, slashing conditions, or signal markets to incentivize performance and penalize failure.
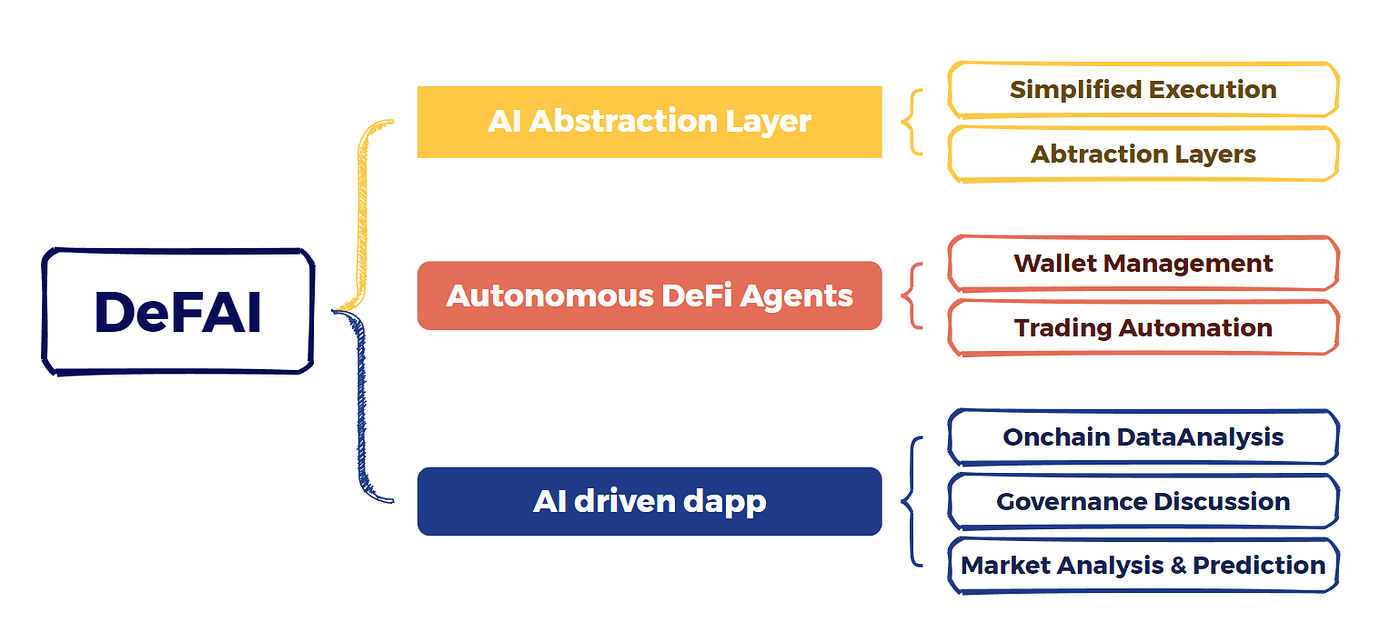
Use Cases & Intelligent Coordination In DeFAI
DeFAI systems are being deployed across multiple financial domains, each emphasizing an aspect of agent-driven automation, capital coordination, or predictive insight. The following use cases highlight how DeFAI is expanding the DeFi landscape:
In autonomous yield optimization, agents dynamically allocate liquidity across multiple protocols or chains to maximize real-time return based on predictive metrics. This replaces static vault strategies with AI-driven rebalancing tools that adapt to changing conditions.
In predictive lending, models use on-chain credit history and off-chain signals to assess borrower risk. They determine loan terms algorithmically and adjust collateral ratios based on probabilistic outcomes, introducing a form of real-time credit intelligence to DeFi lending markets.
In on-chain governance, DeFAI agents analyze community sentiment, treasury metrics, and voter history to generate policy recommendations or even vote autonomously on behalf of stakers who delegate decision-making to trusted models.
In data monetization, users contribute proprietary data (e.g., wallet activity, off-chain preferences) to AI training networks in exchange for tokenized rewards. The agents trained on these datasets fuel downstream DeFAI applications and create feedback loops between data, value, and utility.
Finally, in intent-based execution, DeFAI agents interpret high-level user objectives (e.g., “maximize passive ETH yield this week”) and autonomously execute strategies across protocols. This dramatically simplifies user interaction while preserving DeFi’s trustless properties.
The DeFAI Ecosystem & Emerging Infrastructure
While still in its early phases, the DeFAI ecosystem is rapidly expanding across the Web3 infrastructure stack. Projects such as Autonolas and Allora are pioneering modular agent systems that allow AI agents to perform decentralized operations while being governed by token incentives. These agents can perform actions such as trade execution, strategy rebalancing, or treasury management, all verified through economic consensus.
Bittensor, originally designed as a decentralized machine learning network, provides an on-chain incentive mechanism for training and routing models across subnets, allowing DeFAI systems to tap into open AI intelligence at scale.
Modulus and Ritual are building cryptographic tooling for zkML and verifiable inference, ensuring that AI decisions can be proven correct without exposing proprietary model architecture or user-sensitive data.
Meanwhile, DataHubs and oracle-integrated data markets are forming the informational backbone of DeFAI. These include protocols that price, filter, and package structured and unstructured data for agent consumption, feeding the learning layer that powers adaptive decision-making.
Importantly, DeFAI also influences governance infrastructure. Agents now participate in protocols as on-chain DAO members or treasury managers, introducing algorithmic coordination mechanisms and creating checks against purely human governance that may lack efficiency or scale.
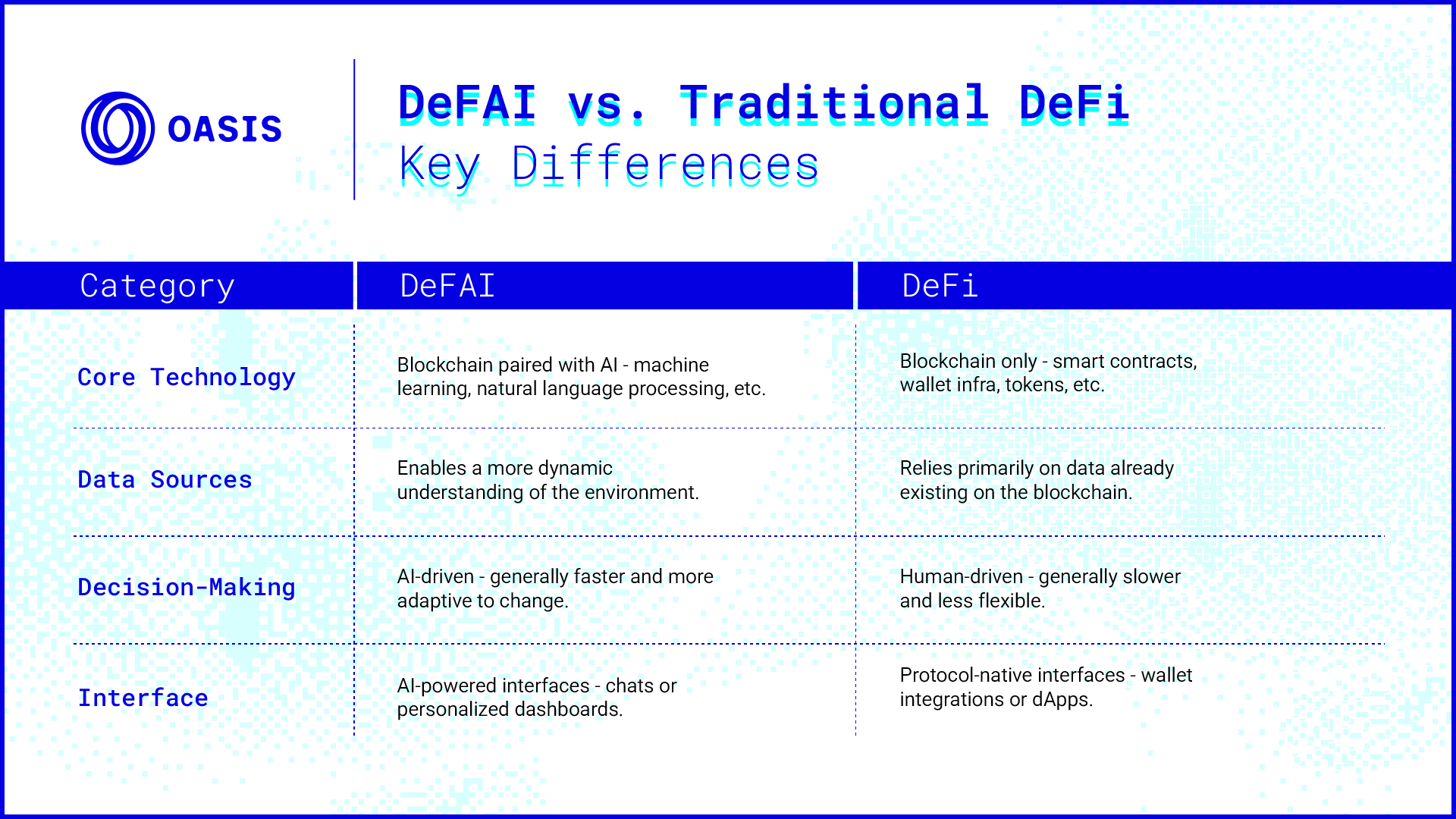
How DeFAI Differs From Traditional DeFi
DeFi is built on the principle of programmable trust: deterministic systems that eliminate middlemen through smart contracts. While it offers transparency and autonomy, traditional DeFi is static. Protocols rarely adapt unless upgraded manually, and users must actively manage risk and exposure.
DeFAI evolves this logic by introducing programmable intelligence. Instead of static conditions, protocols become responsive, learning from behavior, reacting to market shifts, and predicting outcomes before they materialize.
Where DeFi is passive, DeFAI is proactive. Where DeFi relies on user inputs, DeFAI uses agent decision-making. Where DeFi reacts, DeFAI anticipates. These distinctions are not merely operational; they imply a redefinition of how financial protocols engage with risk, opportunity, and governance.
Toward A Self-Optimizing Financial Infrastructure
DeFAI is not just an augmentation of DeFi; it represents the emergence of self-governing financial infrastructure. By combining AI-driven intelligence with decentralized execution, DeFAI introduces a new category of programmable finance that is adaptable, efficient, and capable of real-time optimization at scale.
This model reimagines liquidity provisioning, governance, risk assessment, and data value capture as living processes guided by autonomous agents aligned with user and protocol goals. It pushes DeFi beyond automation toward coordination and foresight, leveraging intelligence not just for yield but also for resilience, fairness, and strategic depth.
As regulatory clarity, agent verifiability, and open model infrastructure improve, DeFAI will likely become an essential layer of the crypto stack. Its promise lies not only in technical innovation but in enabling a financial system where intelligence is native, trust is algorithmic, and coordination is continuous.