
Key Takeaways
- CeDeFi is redefining the boundaries of blockchain-based finance by merging DeFi’s transparency and programmability with centralized systems’ compliance and operational controls. This hybrid structure is enabling a new generation of financial products that are both user-friendly and regulation-ready.
- CeDeFi’s technical foundation rests on a dual-layer architecture. Smart contracts govern decentralized asset flows and automation, while compliance tools, KYC modules, and custodial safeguards operate in parallel to meet legal and institutional requirements.
- Use cases such as staking, stablecoin-based yield strategies, institutional lending, and tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) illustrate CeDeFi’s potential to deliver capital efficiency, trust minimization, and access to traditional yield sources—all within a secure, programmable environment.
- The CeDeFi ecosystem has rapidly matured, encompassing appchains, liquidity routing infrastructure, structured vaults, and permissioned DeFi zones. Platforms like Unizen, BounceBit, and Maple Finance are leading examples of how these models are being applied in production.
- As regulators, institutions, and developers converge on frameworks that support open yet compliant financial systems, CeDeFi is emerging not as a compromise but as a durable, modular blueprint for scalable, globally integrated crypto finance.
The advent of decentralized finance (DeFi) has redefined how capital is pooled, lent, and transacted in a permissionless manner. Yet, despite its rapid innovation, DeFi’s open and trustless nature also exposes it to significant technical, operational, and regulatory risks. On the other end of the spectrum, centralized finance (CeFi) offers user-friendly infrastructure and regulatory clarity but at the cost of transparency and custodial control. CeDeFi, or Centralized Decentralized Finance, has emerged as a hybrid model seeking to reconcile the best of both paradigms. Originally advanced through infrastructure such as BNB Chain and expanded by platforms like Unizen and BounceBit, CeDeFi represents a structural evolution intended to broaden access to blockchain-based finance while meeting compliance and usability demands.
This Innovation and Tech report thoroughly investigates CeDeFi’s structural design, practical implementations, comparative advantages, and future implications. It evaluates whether this model is a transitional framework or a long-term evolution in crypto finance.
What Is CeDeFi? Understanding The Hybrid Finance Model
Centralized-Decentralized Finance (CeDeFi) refers to a hybrid financial model that combines the programmability and transparency of decentralized finance with the oversight and operational efficiency of centralized institutions. CeDeFi platforms aim to deliver compliant, secure, and scalable financial services by embedding identity verification, risk management, and user protection features into on-chain smart contracts and decentralized protocols.
Unlike traditional DeFi, which emphasizes total permissionlessness, CeDeFi introduces regulated gateways and institutional interfaces, such as KYC modules, custodial bridges, and transaction monitoring, without removing the decentralized infrastructure’s open-source and composable nature. This hybrid design allows CeDeFi protocols to support real-world financial use cases, offer cross-border accessibility, and appeal to retail users and institutional capital.
At a structural level, CeDeFi operates through two core components: a decentralized execution layer built on blockchain protocols that handles smart contracts and asset flows, and a centralized integration layer responsible for compliance, fiat access, customer support, and custodial management. The result is a system that upholds the values of decentralization while integrating the practical requirements of modern finance.

How CeDeFi Compares To DeFi & CeFi?
Understanding CeDeFi’s strategic significance helps to compare it to the financial models it blends: DeFi and CeFi. Traditional CeFi platforms such as centralized exchanges or neobanks provide intuitive interfaces, regulatory compliance, and seamless fiat integration. However, they also rely on custodial control and centralized governance, exposing users to counterparty risk and opaque operations, as evidenced by failures like Celsius and FTX.
DeFi, by contrast, offers full user custody and protocol-level automation through smart contracts. It prioritizes transparency, censorship resistance, and borderless participation. Yet it faces persistent challenges, including fragmented liquidity, exploit risk, regulatory uncertainty, and an often steep learning curve for users unfamiliar with Web3 infrastructure.
CeDeFi seeks to merge the best aspects of both: the transparency, programmability, and innovation of DeFi with the user safeguards, reliability, and regulatory pathways of CeFi. For example, a CeDeFi staking platform might allow users to delegate tokens to decentralized validators while offering withdrawal insurance, slashing protection, and fiat on-ramps, all within a regulated interface.
Where DeFi builds on code-as-law, and CeFi relies on institutional trust, CeDeFi proposes a layered governance model: algorithmic and community governance on-chain, combined with off-chain legal contracts and operational controls. This dual structure enables the creation of financial systems that are auditable, adaptable, compliant, and composable at once.

Emerging Infrastructure Trends & Strategic Patterns In CeDeFi
Integration of Appchains & Modular Layer 2 Solutions
The rise of appchains and modular Layer 2 (L2) solutions is enabling institutions to deploy permissioned execution layers atop decentralized settlement chains like Ethereum or Cosmos. This architecture allows for tailored governance and compliance modules while maintaining the composability benefits inherent to public blockchains. By leveraging these modular frameworks, organizations can customize their blockchain environments to meet specific regulatory and operational requirements without sacrificing interoperability.
Enhanced Liquidity Routing Mechanisms
CeDeFi platforms are increasingly adopting sophisticated liquidity routing mechanisms. Centralized exchanges are directing user funds into decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols through vault wrappers or automated market maker (AMM) aggregators. This strategy boosts DeFi’s total value locked (TVL) without necessitating user-level blockchain literacy. By abstracting the complexities of DeFi interactions, CeDeFi platforms are making decentralized financial services more accessible to a broader audience.
Advancement of Algorithmic Governance Models
Algorithmic governance within CeDeFi is becoming more nuanced and sophisticated. Hybrid platforms are implementing on-chain decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) that govern protocol parameters, while operational entities handle execution and compliance. This dual-governance framework blends the transparency and community involvement of decentralized governance with the accountability and regulatory adherence of centralized oversight. Such models aim to balance innovation with stability, ensuring that CeDeFi platforms can adapt to evolving market dynamics and regulatory landscapes.
These trends collectively indicate a maturation of the CeDeFi ecosystem, highlighting its potential to bridge the gap between traditional financial systems and decentralized technologies. As CeDeFi continues to evolve, it is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of finance, offering solutions that combine the best aspects of centralized and decentralized paradigms.
Technical Architecture & Operation of CeDeFi Protocols
The architecture of CeDeFi (Centralized Decentralized Finance) systems is designed to strike a balance between permissionless innovation and institutional-grade control. Rather than operating as either a purely decentralized or purely custodial system, CeDeFi platforms integrate a two-layered architecture with clearly defined roles for both decentralized and centralized components. This dual-stack model enhances usability, regulatory compliance, and systemic resilience.
At the foundation of CeDeFi protocols lies the decentralized execution layer. This layer includes smart contracts deployed on public blockchains, typically on Layer 1 (e.g., Ethereum) or Layer 2 networks, that perform the core financial functions. These contracts manage on-chain activities such as liquidity provisioning, lending pools, staking rewards, and price discovery through AMMs or oracles. The smart contract logic is open-source, auditable, and often governed by token-based voting, giving users transparency and immutability in core operations.
Overlaying this is the centralized integration and compliance layer, responsible for functions that cannot yet be fully decentralized due to regulatory, legal, or practical constraints. These include Know Your Customer (KYC) verification, risk profiling, transaction monitoring, and fiat gateway integration. Platforms like BounceBit, for example, deploy decentralized infrastructure for Bitcoin restaking and cross-chain yield generation, while also embedding compliance-friendly identity verification and custodial guardrails to meet institutional standards.
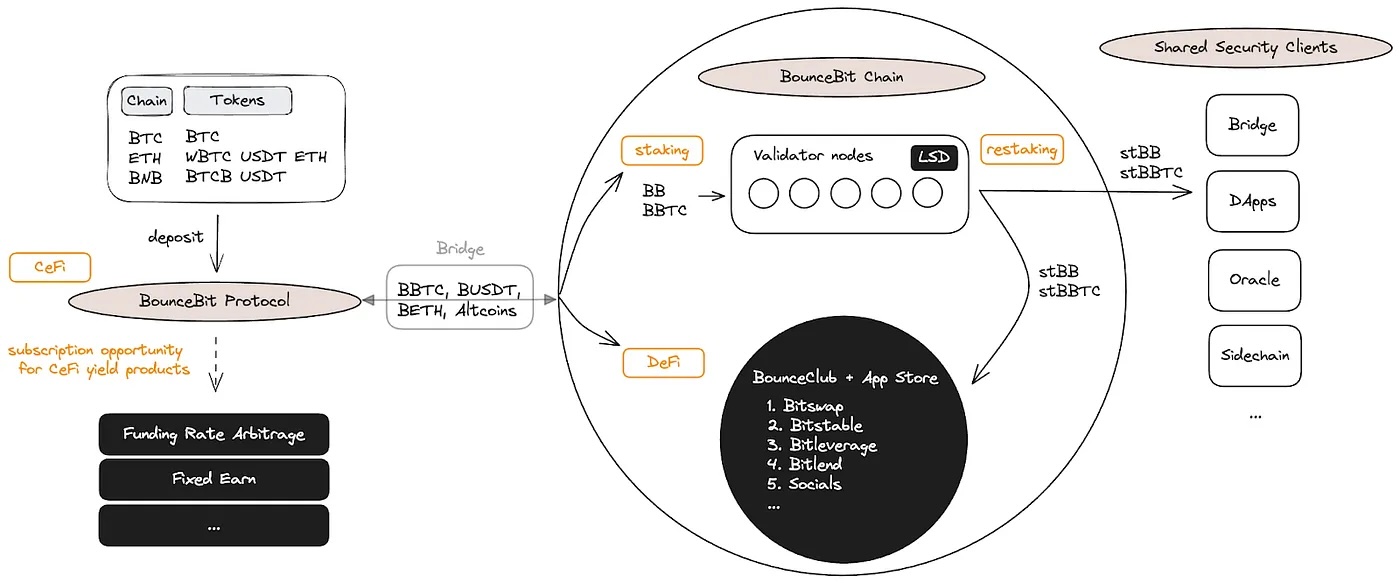
A critical innovation within some CeDeFi architectures is the concept of permissioned zones within decentralized networks. In this model, certain users, typically institutional participants, interact with the same on-chain contracts as retail users but do so through whitelisted addresses that adhere to predefined compliance protocols. Meanwhile, open access is preserved for non-restricted retail participants through separate interface layers or policy-bound smart contract endpoints.
CeDeFi also supports modular extensions, such as policy-based vaults, reputation-weighted liquidity access, or even intent-based execution logic. This flexibility enables institutions to use standardized DeFi primitives while embedding enterprise-specific governance, performance analytics, or risk caps, bridging the institutional gap that DeFi alone struggles to accommodate.
Key Implementations & Use Cases of CeDeFi In Practice
CeDeFi has begun to reshape several high-impact domains within the broader crypto-financial landscape, including staking, lending, stablecoin issuance, and real-world asset (RWA) tokenization. These implementations demonstrate how hybrid models can provide risk-mitigated, user-friendly, and regulation-aware access to yield-generating activities while maintaining the composability and programmability of decentralized systems.
One of the most visible use cases for CeDeFi is in staking and validator delegation, where centralized exchanges and custodial platforms act as intermediaries between users and decentralized staking protocols. While the underlying staking mechanics may rely on protocols like Lido or Rocket Pool, the user’s interaction with the service is typically abstracted. Exchanges such as Coinbase, Kraken, and others offer custodial staking products that allow users to earn yield without directly managing their staking infrastructure. These platforms may assume slashing risk, offer guaranteed uptime, and support user withdrawal liquidity while settling to decentralized protocols in the background. This CeDeFi structure lowers the technical barrier to participation in proof-of-stake networks while maintaining the benefits of decentralized security and yield.
In the lending and borrowing sector, hybrid platforms like Nexo and Matrixport are examples of CeDeFi in action. These firms often use smart contracts to enable lending pools and real-time interest calculations, but manage user deposits in custodial wallets. Borrowing limits, collateral ratios, and liquidation thresholds are governed not only by code but also by centralized risk frameworks modeled after traditional finance. These platforms typically provide fiat bridges, institutional-grade insurance coverage, and transparency reports, making them accessible to retail and regulated financial actors. Through this model, CeDeFi is enabling capital-efficient access to yield and credit without exposing users to the full complexities or risks of DeFi-native protocols.
Stablecoin integration is another essential dimension of CeDeFi’s utility. Platforms that support fiat-backed stablecoins like USDC, EURC, and USDP increasingly operate in CeDeFi environments that include compliance-layer monitoring and regulatory reporting. These stablecoins serve as base assets for structured products, liquidity provision, and yield farming strategies—all within a governance model that adheres to global anti-money laundering (AML) standards. CeDeFi protocols incorporating stablecoin rails benefit from enhanced liquidity and credibility, allowing them to service crypto-native and fiat-anchored market participants.
Perhaps one of the most transformative CeDeFi use cases is the tokenization and on-chain distribution of real-world assets (RWAs). Protocols like Ondo Finance and Maple Finance are pioneering this frontier by deploying capital into tokenized U.S. Treasuries, investment-grade bonds, and enterprise credit lines. Ondo’s OUSG and Maple’s secured lending products allow asset managers to earn real-world yields via permissioned smart contracts backed by off-chain legal agreements. These instruments use on-chain interfaces to provide transparency and automated execution while anchoring real-world risk through audited counterparties and legal contracts. This combination of real-world compliance and DeFi automation enables asset classes once exclusive to institutional finance to become programmable, fractional, and globally accessible through CeDeFi rails.
Collectively, these use cases reveal how CeDeFi is not merely a compromise between CeFi and DeFi, but a gateway for building bridges between them. By combining legal enforceability, regulatory compliance, and DeFi composability, CeDeFi models are enabling the evolution of capital markets into programmable ecosystems, offering solutions that are simultaneously transparent, secure, and institutionally viable.
Mapping The CeDeFi Ecosystem: Platforms, Protocols, & Application Layers
The CeDeFi ecosystem has expanded rapidly over the past two years, fueled by growing interest from institutions seeking access to DeFi yields without sacrificing compliance or usability. The sector now includes a diverse set of platforms ranging from hybrid exchanges to structured product vaults, each operating within the CeDeFi design philosophy. Rather than replicating the DeFi ecosystem, CeDeFi protocols selectively borrow and reengineer their components with modularity and compliance in mind.
One of the most prominent examples is Unizen, which brands itself as a Smart Exchange Ecosystem. Unizen integrates centralized liquidity with access to decentralized protocols via a single interface, allowing users to interact with DEXs while onboarding through centralized flows that meet regulatory standards. The platform provides portfolio rebalancing, trade aggregation, and KYC-compliant execution, all underpinned by decentralized routing logic and data analytics.
Meanwhile, BounceBit illustrates CeDeFi’s cross-chain potential. Its core infrastructure enables Bitcoin holders to participate in DeFi-like yield strategies without bridging or wrapping assets. Through restaking and delegated participation frameworks, BounceBit provides an execution layer that runs on smart contracts while safeguarding base-layer security and introducing custodial fallback layers in case of network disputes. This design addresses one of the key frictions in traditional DeFi, capital mobility from non-EVM chains.
The asset management layer of CeDeFi is also evolving. Platforms like TProtocol and Ribbon Finance have launched compliant structured vaults offering yield strategies derived from options and interest rate swaps. While these platforms began in the DeFi space, many are now building regulatory-compliant frontends or integrating whitelisted wallet functionality for onboarding traditional capital.
On the lending and credit side, protocols such as Maple Finance and Centrifuge operate as capital marketplaces where KYC-compliant borrowers issue tokenized debt obligations to lenders. While these aren’t fully centralized, they represent the synthesis of on-chain credit issuance with off-chain legal enforceability, an emerging hallmark of CeDeFi.
The infrastructure side of CeDeFi also includes custodial bridges, data compliance layers, and risk scoring engines. Providers like Fireblocks and Ledger Enterprise are enabling secure key management and institutional wallet systems that integrate with CeDeFi protocols to facilitate direct on-chain engagement by fund managers and asset allocators.
In total, the CeDeFi ecosystem is not a single network or category but a multi-layered stack of infrastructure, middleware, and application-level services that collaborate to enable compliant, programmable finance. The continued expansion of this stack signals the increasing demand for decentralized and integrable financial systems into existing regulatory and operational frameworks.
CeDeFi As A Blueprint For Regulated, Scalable Crypto Finance
CeDeFi is no longer a theoretical bridge between two financial paradigms; it is evolving into a foundational architecture for the next generation of digital markets. By reconciling the core principles of decentralization with the operational needs of regulated institutions, CeDeFi offers a framework that is both adaptive and future-ready.
Its layered infrastructure, combining permissionless execution with compliance-aware interfaces, reflects a growing recognition that innovation and regulation are not mutually exclusive. Through applications in staking, stablecoin yield strategies, tokenized real-world assets, and institutional lending, CeDeFi is proving capable of delivering real economic value without sacrificing transparency or accessibility.
As the crypto industry matures and regulatory scrutiny intensifies, models like CeDeFi will be critical in legitimizing decentralized finance within broader financial systems. Its success will depend on sustained innovation in governance, cross-chain infrastructure, and risk management, but the direction is clear. CeDeFi is not a stopgap. It is a structural evolution, offering a modular and durable path forward for programmable, compliant global finance.






