Key Takeaways
- NFTs Defined: Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are unique blockchain-based assets that verify digital ownership, ensuring authenticity and scarcity for digital and physical items.
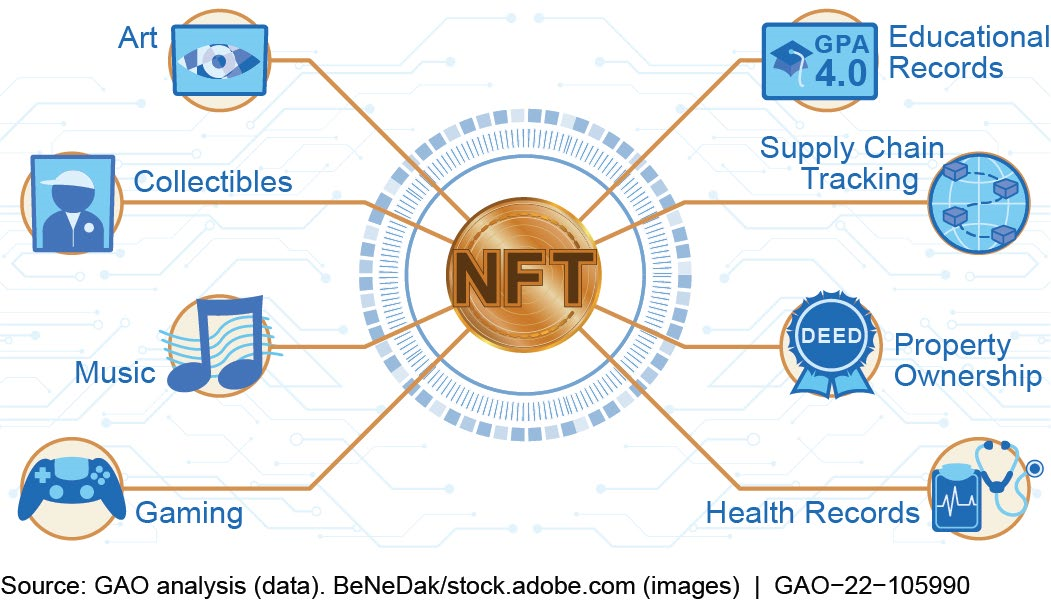
- Diverse Applications: NFTs transform art, gaming, real estate, and identity management by tokenizing assets, enhancing liquidity, and enabling decentralized ecosystems.
- Economic Impact: NFTs empower creators with direct monetization and 5-10% perpetual royalties, with 2024 data showing NFT artists earning 3.2 times more than traditional digital artists.
- Technical Challenges: Security vulnerabilities, metadata risks, and regulatory uncertainties persist, though decentralized storage and formal verification tools are mitigating issues.
- Future Growth: By 2025, NFTs will integrate with AI, IoT, and metaverse platforms, driving a $14.9 billion gaming NFT market and shaping Web3’s digital property rights.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) represent a groundbreaking application of blockchain technology, redefining ownership, authenticity, and value exchange in the digital era. By leveraging cryptographic uniqueness, non-fungible tokens enable verifiable digital scarcity, revolutionizing industries such as art, gaming, real estate, and identity management. This Innovation and Tech article provides a comprehensive analysis of NFTs, covering their fundamentals, historical evolution, applications, challenges, and future trajectories, emphasizing their role in fostering decentralized economies and driving Web3 innovation through 2025.

NFT Technology & Fundamentals Of NFTs
NFTs are cryptographic tokens stored on a blockchain, representing ownership of unique digital or physical assets. Unlike fungible cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, each NFT contains distinct metadata, ensuring non-interchangeability and immutable provenance tracking. Built primarily on Ethereum using token standards such as ERC-721 for individual uniqueness and ERC-1155 for hybrid fungible and non-fungible assets, NFTs integrate with decentralized storage solutions like InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) and Arweave to secure metadata. Smart contracts automate ownership transfers and enforce programmable features, such as royalties.
This technological framework addresses the digital originality problem, establishing non-fungible tokens as a trustless, transparent system for true digital possession, akin to physical property rights.
NFTs: Historical Evolution
The origins of NFTs trace back to early blockchain experiments. In 2012, Colored Coins on Bitcoin attempted to represent real-world assets, followed by the Counterparty Protocol’s 2014 trading cards. Kevin McCoy’s “Quantum” (2014), minted on Namecoin, is recognized as the first true non-fungible token, showcasing blockchain’s potential for digital art. The 2017 release of Ethereum’s ERC-721 standard catalyzed mainstream adoption, with CryptoPunks (10,000 unique avatars) and CryptoKitties (a breeding game that congested Ethereum’s network) proving their viability.
The 2021 market surge, marked by Beeple’s $69 million “Everydays” sale at Christie’s, propelled the non-fungible token market capitalization from $82 million to $17 billion. Since 2022, the ecosystem has matured, with dynamic standards like ERC-998 for composable NFTs, hybrid physical-digital assets from luxury brands, and regulatory frameworks like the EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) shifting focus from speculation to utility-driven applications.
Applications & Use Cases
Creative Economies
NFTs have democratized creative industries by enabling artists, musicians, and writers to monetize directly through blockchain-based marketplaces. Programmable royalties, typically 5-10% on secondary sales, ensure perpetual revenue streams. A 2024 study found NFT artists earn 3.2 times more than traditional digital artists, driven by these royalties and direct consumer sales. Generative algorithms have birthed new art forms, such as algorithmically created visuals and music, expanding creative boundaries. Platforms like OpenSea and Rarible facilitate these transactions, fostering a decentralized creator economy that bypasses traditional intermediaries.
Asset Tokenization
NFTs tokenize real-world assets (RWA), enhancing liquidity, transparency, and accessibility. In real estate, fractional ownership allows investors to purchase shares of properties, democratizing access to high-value markets. Luxury brands, such as Gucci and Louis Vuitton, use them to combat counterfeiting by linking physical goods to blockchain-verified tokens. In pharmaceuticals, they verify drug authenticity, reducing an estimated $98 billion in annual counterfeit losses. Supply chain applications further leverage NFTs for provenance tracking, ensuring transparency from raw materials to end products, particularly in food safety and electronics.
Gaming & Metaverse
In gaming, they represent in-game assets, such as characters, skins, and weapons, enabling player-owned economies. Games like Axie Infinity and The Sandbox allow users to trade and monetize virtual assets, creating new revenue models. Metaverse platforms, including Decentraland, trade virtual land parcels, with 2024 transactions averaging $2.4 million per parcel. These trends align with Web3’s user-owned internet philosophy, positioning NFTs as digital heirlooms, with 34% of Millennials and Gen Z preferring NFT collectibles over physical assets, according to a 2024 survey.
Identity & Governance
NFTs enable decentralized identity systems, such as Soulbound tokens, which are non-transferable credentials for education, employment, or reputation. These tokens empower users to control their data while ensuring privacy and authenticity. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) use NFT-based membership for community governance, allowing token holders to vote on proposals and shape platform policies. Applications in digital certificates and gaming identifiers, such as “Proof of Personhood,” further prevent fraud and enhance user trust in decentralized ecosystems.
Technical Challenges Surrounding NFTs & Their Solutions
Security Vulnerabilities
Despite blockchain’s inherent security, NFT ecosystems face significant risks. In 2024, 1,331 defective smart contracts and 7,487 fraudulent projects, known as “rug pulls,” were identified, undermining user trust. Metadata decoupling affects 68% of NFT art, risking link rot if centralized servers fail. Solutions include formal verification tools, such as NFTGuard, which audit smart contracts for vulnerabilities, and increased adoption of decentralized storage protocols like IPFS to ensure metadata permanence. Multi-signature wallets and enhanced user education are also reducing phishing and scam vulnerabilities.
Environmental Impact
Ethereum’s pre-Merge Proof-of-Work consensus consumed 0.34TWh monthly, equivalent to the energy use of a small nation. Its 2022 transition to Proof-of-Stake reduced energy consumption by 99.95%, addressing environmental criticisms. Eco-friendly blockchains, such as Polygon (0.00079kWh per transaction) and Solana, are increasingly adopted for sustainable NFT projects. Layer-2 solutions, including rollups, further minimize energy demands while maintaining scalability, ensuring NFTs align with global sustainability goals.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Regulatory ambiguity poses a significant challenge. Jurisdictional conflicts over whether NFTs are securities, collectibles, or commodities create legal uncertainties. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission has 16 ongoing lawsuits against NFT marketplaces, focusing on unregistered securities offerings. The proposed U.S. NFT Act seeks to clarify definitions and protections for art and collectible NFTs, yet only 12% of current NFT licenses clearly define commercial usage terms, leading to intellectual property disputes. Globally, the EU’s MiCA framework provides a model for consumer protection, but harmonized regulations remain elusive.
Future Trends & Innovations
Technological Convergence
By 2025, NFTs will integrate with emerging technologies to unlock new use cases. The ERC-7857 standard enables transferable AI models, allowing creators to monetize AI-generated art with provable originality. Internet of Things (IoT) interactions will see NFT-tagged physical assets communicate via smart contracts, enhancing supply chain automation. Zero-knowledge proofs, such as zk-SNARKs, will enable privacy-preserving ownership verification, supporting applications like anonymous digital identity and secure voting systems. These advancements position NFTs at the forefront of Web3 innovation.
Market Growth
Market projections for 2025 indicate robust growth across sectors. Gaming NFTs are expected to reach a $14.9 billion market with a 39% compound annual growth rate, driven by play-to-earn models. Enterprise adoption is accelerating, with 73% of Fortune 500 companies testing NFT-based loyalty programs to enhance customer engagement. Decentralized finance (DeFi) integration is projected to facilitate $7 billion in NFT-collateralized loans, leveraging NFTs as loanable assets. However, speculative art markets have contracted, with trading volumes down 93% from 2021 peaks, signaling a shift toward utility-driven NFTs.
Sociotechnical Implications
Long-term, NFTs will underpin transformative systems. Soulbound tokens will support digital identity frameworks, enabling secure, user-controlled credentials for education and employment. Microtransaction-enabled content monetization, with granularity as low as 0.0001 cents, will empower creators to monetize niche content, such as blog posts or short videos. Evolving legal frameworks will address copyright infringement, with blockchain-based licensing ensuring clear ownership rights. As IBM researchers state, NFTs represent the logical evolution of property rights in the digital frontier, cementing their role in decentralized ecosystems.
The Future Of Digital Ownership & Web3 Innovation
Non-fungible tokens have evolved from a speculative novelty to a foundational technology for the ownership economy. By enabling verifiable digital scarcity, NFTs bridge physical and digital realms, transforming creative industries, asset management, gaming, and identity systems. Ongoing innovations in blockchain infrastructure, smart contracts, and regulatory frameworks are addressing critical challenges in security, sustainability, and legal clarity. As integrations with AI, IoT, and metaverse platforms accelerate, NFTs will anchor digital property rights, reshaping how society creates, owns, and transfers value. Through 2025 and beyond, NFTs will remain a cornerstone of Web3 innovation, driving decentralized, user-centric systems across the global economy.