
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain Technology Defined: Blockchain technology is a decentralized, secure digital ledger that ensures transparency and immutability, revolutionizing industries from cryptocurrencies to supply chains.
- Diverse Applications: Blockchain applications span cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, supply chain transparency, healthcare data security, and digital identity, driving efficiency and trust across sectors.
- Scalability Challenges: The blockchain trilemma—balancing decentralization, security, and scalability—limits transaction throughput, but solutions like Layer-2 networks and sharding are enhancing performance.
- Regulatory Evolution: Global regulations, such as the EU’s MiCA and proposed U.S. stablecoin frameworks, are shaping blockchain technology’s adoption, with varied approaches impacting market growth by 2025.
- Future Innovations: Integration with AI, IoT, and DePIN projects, alongside institutional adoption, positions blockchain technology to transform finance, infrastructure, and data management by 2032.
Blockchain technology has evolved significantly since its introduction with Bitcoin in 2008, transforming from a cryptocurrency foundation to a revolutionary force spanning numerous industries. As a decentralized digital ledger, blockchain technology ensures secure, transparent, and immutable record-keeping, disrupting traditional systems with its innovative approach.
This Innovation and Tech report examines the fundamentals, applications, challenges, and future trends of blockchain technology, with particular attention to developments expected through 2025, highlighting its potential to reshape finance, healthcare, supply chains, and beyond.
Fundamentals Of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that securely stores records across a computer network, ensuring transparency, immutability, and resistance to tampering. Each “block” contains data, linked in a chronological “chain.” Unlike centralized databases, blockchain operates as a distributed system with data stored across multiple computers, making it tamper-resistant. Its layered architecture includes infrastructure (hardware), networking (node discovery, information propagation), consensus mechanisms (proof of work, proof of stake), data (blocks, transactions), and applications (smart contracts, decentralized applications).
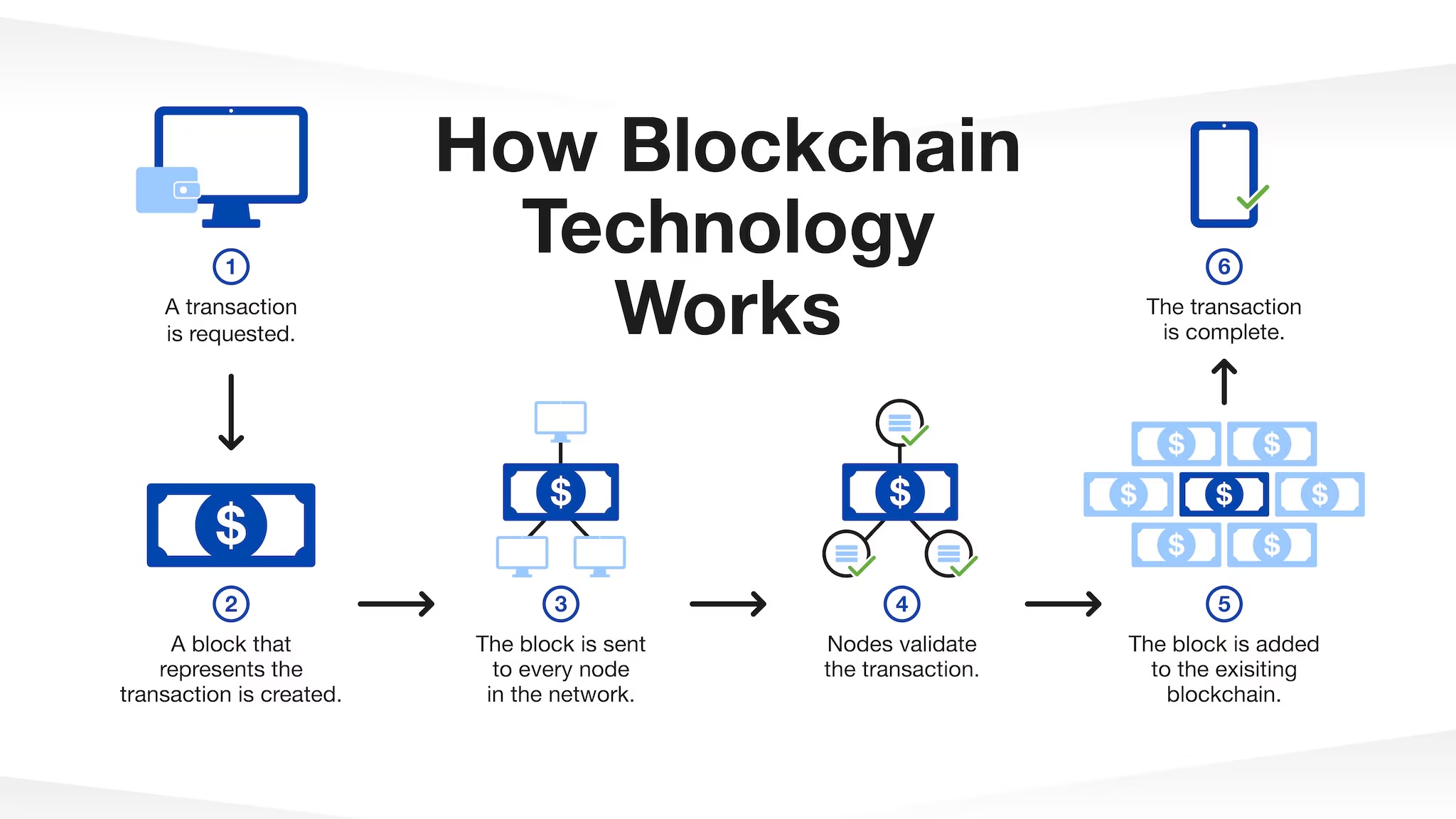
These layers enable blockchain technology’s core characteristics: security, transparency, and decentralization. Transactions are validated through consensus mechanisms, grouped into blocks, and linked using cryptographic techniques, forming a secure chain. This structure ensures data integrity, positioning blockchain technology as a “tamper-evident and tamper-resistant digital ledger implemented in a distributed fashion.”
The key benefit of blockchain technology lies in its ability to provide security and trust without traditional intermediaries like banks. Traditional databases face challenges in trust and security, but blockchain creates a secure, members-only network, ensuring accurate data access while restricting confidential records to authorized users. When a transaction occurs, it is broadcast to a peer-to-peer network, validated using consensus algorithms, combined into a new block, and added to the blockchain as a permanent, immutable record, completing the transaction seamlessly.

Applications & Use Cases Of Blockchain Technology

Cryptocurrency & Financial Services
The most prominent blockchain application is cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, where blockchain technology enables secure peer-to-peer transfers of digital assets without intermediaries. Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain in finance supports efficient money transfers, reduced transaction fees, and increased financial inclusion. Advanced applications include managing slippage in cryptocurrency trading—a challenge where trades execute at prices different from expectations. Traders use limit orders, strategic timing, order splitting, and algorithmic tools like Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP) to minimize slippage, leveraging blockchain technology’s transparency to optimize trading strategies.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, a transformative blockchain application, are digital agreements stored on a blockchain that execute automatically when conditions are met, eliminating intermediaries. Applicable in real estate (automating property transfers), insurance (processing claims), and supply chains (triggering payments), smart contracts enhance efficiency by reducing paperwork and disputes. Blockchain technology’s rule-based execution ensures reliability, making smart contracts a cornerstone of decentralized systems across industries.
Supply Chain & Logistics
Blockchain technology provides unprecedented transparency in supply chains, creating immutable records of products’ journeys from origin to consumer. It reduces counterfeiting through verifiable authenticity, improves inventory management with real-time tracking, enhances consumer trust via transparent sourcing, and streamlines cross-border trade documentation. These capabilities are vital in pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and food safety, where blockchain applications ensure provenance and reliability.
Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain technology secures patient records, verifies medication authenticity, and facilitates secure data sharing across institutions. Research highlights blockchain’s ability to streamline interoperability, guarantee record authenticity, and safeguard patient privacy. Applications include patient-controlled image sharing, multi-institutional research, AI integration, and pharmaceutical supply chain verification, positioning blockchain technology as a game-changer for healthcare efficiency and security.
Digital Identity
Blockchain-based identity systems empower users to control their data, track its usage, and share information securely, reducing identity theft and fraud. Unlike vulnerable traditional systems, blockchain identity solutions are both public and private, enabling peer-to-peer transactions with consensus-driven security. Applications include digital certificates for employment and unique identifiers in gaming to prevent cheating, with “Proof of Personhood” gaining traction to verify human-driven interactions in an AI-heavy digital landscape.
Real-World Asset Tokenization
Tokenizing real-world assets (RWA) is a promising blockchain application, representing assets like real estate, stocks, bonds, and commodities as blockchain-based tokens. This enhances liquidity, transparency, and accessibility through fractional ownership, with smart contracts automating transactions. Sectors adopting RWA include real estate (tokenized property shares), financial markets (blockchain-based securities), and commodities (efficient trade management), showcasing blockchain technology’s potential to democratize investment.
Technical Challenges & Solutions In Blockchain Technology
The Blockchain Trilemma
A core challenge in blockchain technology is the “blockchain trilemma,” balancing decentralization, security, and scalability. Traditional blockchains like Bitcoin (7-10 transactions per second) and Ethereum face scalability limits due to designs prioritizing decentralization and security. Bitcoin’s 1 MB block size and 10-minute block creation time restrict throughput compared to systems like Visa, which handle thousands of transactions per second, highlighting the need for scalable blockchain solutions.
Scalability Solutions
To address scalability, blockchain technology is evolving with Layer-2 solutions (e.g., Lightning Network, rollups) for near-instant, low-fee transactions, sharding to split blockchains into manageable pieces, and alternative consensus mechanisms requiring less computational power than proof-of-work. Layer-2 networks, operating atop existing blockchains, are seeing faster adoption, alleviating congestion and high fees on platforms like Ethereum, enhancing blockchain technology’s efficiency.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount in blockchain technology, especially for IoT applications. Blockchain’s distributed nature—exemplified by Bitcoin’s records across thousands of servers—makes breaches nearly impossible, requiring simultaneous manipulation of 51% of nodes. Ongoing research focuses on data privacy, secure communication protocols, and integrating blockchain with IoT to prevent data duplication and enhance system integrity, ensuring robust blockchain applications.
Trends & Future Developments For Blockchain Technology By 2025
Regulatory Frameworks
Regulation shapes blockchain technology’s trajectory, with the EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) setting a global standard for consumer protection and market integrity. In the U.S., 2025 initiatives, including a proposed bicameral crypto committee and stablecoin bill, aim to foster innovation and market integrity. However, global approaches vary—China’s bans contrast with El Salvador’s Bitcoin adoption, highlighting the fragmented regulatory landscape impacting blockchain technology’s growth.
AI Integration With Blockchain
The convergence of AI and blockchain technology is unlocking new possibilities in secure data management and automation. By 2025, AI agents may autonomously manage crypto wallets, leveraging zero-knowledge proofs for privacy, decentralized training models for reduced bias, and complex smart contract automation. Applications span healthcare (secure AI diagnostics), cybersecurity (anomaly detection), and supply chains (optimized logistics), positioning blockchain technology at the forefront of innovation.
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN)
DePIN projects use blockchain technology to decentralize infrastructure like internet networks, energy grids, and cloud computing. Though early traction was limited, their potential to transform telecommunications and utilities via transparent, community-driven systems is growing. Decentralized Autonomous Utility Tokens (DePUT) could revolutionize public utility funding, showcasing blockchain applications in physical infrastructure.
Microtransactions & Future Payment Systems
Blockchain technology enables low-cost microtransactions, overcoming traditional systems’ high fees and delays. Applications include content monetization (pay-per-view models), gaming (in-game purchases), and machine-to-machine payments (IoT devices paying for services). Stablecoins facilitate instant cross-border enterprise payments, while blockchain-based government bonds could enhance financial transparency, expanding blockchain technology’s role in payments.
Blockchain In Internet Of Things (IoT)
Blockchain technology enhances IoT security by securing connected device networks, preventing data duplication, and ensuring privacy. Its distributed structure makes it ideal for secure device communication, with applications in smart cities and industrial IoT, reinforcing blockchain’s versatility beyond financial use cases.
Institutional Adoption & Market Growth
Institutional adoption of blockchain technology is surging, with bitcoin ETFs legitimizing digital assets in portfolios. A reported 93% of industry leaders believe in blockchain’s long-term value, and IBM forecasts the blockchain market to grow to nearly 1 trillion U.S. dollars by 2032 at a 56.1% CAGR since 2021. This reflects growing confidence from traditional finance and startups, driving blockchain technology’s mainstream integration.
Advanced Slippage Management In Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology supports innovative slippage management in crypto trading, with frameworks like the Cascading Waterfall Round Robin Rebalancing Mechanism optimizing trade execution. Deep learning advances predict slippage, and increased institutional participation boosts liquidity, narrowing price gaps and enhancing market efficiency, underscoring blockchain’s role in refining financial systems.
Shaping The Future With Blockchain: Transformative Insights
Blockchain technology has evolved from its cryptocurrency origins to become a transformative force across numerous industries. Its fundamental characteristics of security, transparency, and decentralization make it invaluable for applications ranging from finance and healthcare to supply chain management and digital identity. Looking toward 2025, blockchain technology is poised for significant advancements in regulatory frameworks, institutional adoption, and technological innovations.
The integration of blockchain with emerging technologies like AI and IoT will likely open new possibilities, while solutions to challenges like scalability will enhance its practical utility. As industry experts note, “By 2025, the transformation of blockchain, AI, and digital commerce will be nothing short of revolutionary.” While challenges remain in regulation, scalability, and security, the continued evolution of blockchain technology promises to reshape how we conduct transactions, manage data, and build trust in digital systems across the global economy.






