Key Takeaways
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK) enable privacy and security in cryptocurrency by proving statements without revealing underlying data.
- ZK-Rollups, a Layer 2 solution, enhance blockchain scalability by processing transactions off-chain with succinct on-chain proofs.
- zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs are key ZK implementations, with zk-SNARKs powering privacy-focused ledgers like Zcash.
- Recent innovations like CrowdProve and proof of storage improve decentralization and data availability in ZK-Rollups.
- ZK applications extend beyond scaling to financial privacy, distributed key generation, and proof of assets for exchanges.
Zero-Knowledge proofs (ZK) have emerged as a transformative technology in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, enabling enhanced privacy, security, and scalability. These cryptographic protocols allow one party to prove to another that a statement is true without revealing any additional information beyond the validity of the statement itself. This Innovation and Tech report explores the fundamentals of Zero-Knowledge proofs, their applications in cryptocurrency, particularly in the form of ZK-Rollups, and examines their future potential in blockchain systems.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Fundamentals & Cryptography
Zero-Knowledge proofs represent a sophisticated branch of cryptography that enables verification without disclosure of underlying data. A ZK proof allows a prover to demonstrate possession of certain information (such as a solution to a computational problem) without revealing the content of that solution. The core properties that define a valid Zero-Knowledge proof include completeness (if the statement is true, an honest verifier will be convinced), soundness (if the statement is false, no cheating prover can convince an honest verifier), and zero-knowledge (the verifier learns nothing beyond the validity of the statement).
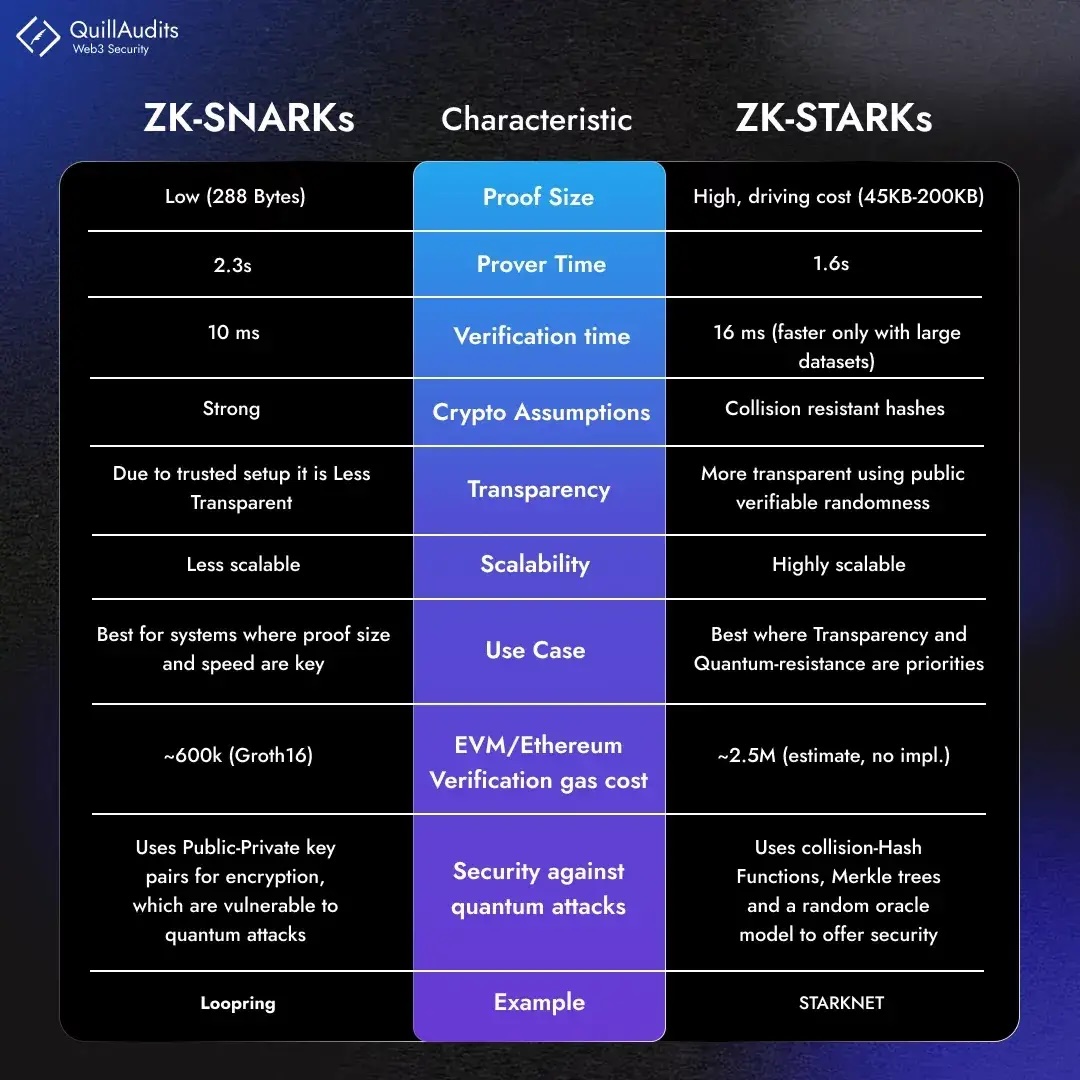
The most prominent implementation in cryptocurrency contexts is the zk-SNARK (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge), a protocol that allows for verification without interaction between prover and verifier. This non-interactive property makes zk-SNARKs particularly suitable for blockchain applications where direct interaction between parties isn’t feasible. The technology builds upon sophisticated mathematical constructs, including Quadratic Arithmetic Programs and specialized cryptographic protocols like Pinocchio. While traditional interactive ZK proofs were impractical for blockchain implementation, zk-SNARKs have enabled privacy-preserving ledgers like Zcash and contributed to numerous scaling solutions.
Recent research has expanded the ecosystem to include alternative implementations such as zk-STARKs (Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge) and zk-Fabric, which provides a polylithic syntax for zero-knowledge joint proof systems. These variations offer different trade-offs regarding proving time, verification time, and cryptographic assumptions.
ZK-Rollups: Revolutionizing Blockchain Scalability
Blockchains like Ethereum face fundamental scalability challenges that limit their widespread adoption. ZK-Rollups have emerged as a leading Layer 2 scaling solution that leverages Zero-Knowledge proofs to address these limitations. These systems process transactions off-chain and then publish succinct proofs on the main blockchain, allowing verification of thousands of transactions with a single compact proof.
ZK-Rollups operate by batching multiple transactions off-chain, generating cryptographic proofs of their validity, and then posting these proofs along with compressed transaction data to the main blockchain. This approach significantly increases transaction throughput while inheriting the security guarantees of the underlying blockchain. The architecture of ZK-Rollups typically involves sequencers that order transactions, provers that generate validity proofs, and smart contracts on the main chain that verify these proofs.
Recent implementations include Polygon zkEVM and zkSync Era, which have been subjected to comprehensive benchmarking to evaluate their efficiency and performance trade-offs. These systems represent a significant advance in blockchain scalability, achieving transaction speeds orders of magnitude higher than base layer processing while maintaining strong security properties.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Recent Innovations & Research
Research into ZK-Rollups has accelerated dramatically, with numerous innovations emerging in recent months. The CrowdProve system, introduced in January 2025, addresses the centralization concerns in ZK-Rollup proving by enabling distributed proof generation across a community of small provers. This approach maintains performance comparable to centralized systems while enhancing the decentralization properties that are fundamental to blockchain philosophy.
Another significant development is the introduction of “proof of download” and “proof of storage” concepts to address data availability challenges in Layer 2 networks. These mechanisms ensure that transaction data remains accessible and cannot be maliciously deleted, a critical requirement for the security of off-chain scaling solutions. Additionally, innovative role separation techniques allow nodes with limited hardware to participate in Layer 2 networks, further enhancing decentralization.
Applications Beyond Scaling
While scaling represents the most prominent application of ZK technology in cryptocurrency, the versatility of Zero-Knowledge proofs extends to numerous other use cases. Financial privacy applications leverage ZK proofs to enable confidential transactions without compromising the verification capabilities essential to blockchain systems.
Distributed Key Generation (DKG) protocols using smart contracts and zk-SNARKs enable threshold cryptosystems while reducing computational costs by moving complex calculations off-chain. This approach ensures the correct execution of the protocol through on-chain verification while enabling dynamic participation and providing crypto-economic incentives for honest behavior.
ZK technology has also been applied to proof of assets protocols for cryptocurrency exchanges. These systems allow exchanges to demonstrate ownership of sufficient assets to cover customer deposits without revealing sensitive information about specific addresses or balances. This enhances transparency in the exchange ecosystem without compromising security or competitive positioning.

Challenges & Future Directions For Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Despite their promise, ZK-Rollups face significant challenges. Performance bottlenecks remain a concern, particularly regarding the computational intensity of generating Zero-Knowledge proofs. The efficiency of ZK-friendly primitive operations, such as hash functions optimized for ZK circuits, represents an active area of research. Traditional cryptanalysis tools developed for binary fields (F₂ⁿ) cannot be directly applied to the prime fields (Fₚ) typically used in ZK applications, creating security analysis challenges.
Transaction fee mechanisms (TFMs) for ZK-Rollups also require careful design to account for the unique cost structures involving sequencing, data availability, and ZK proving. Creating incentive-compatible and profitable mechanisms remains an open research question with significant implications for the economic sustainability of these systems.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Driving The Next Wave of Blockchain Advancements
Zero-Knowledge proofs have evolved from theoretical cryptographic constructs to practical tools addressing critical challenges in cryptocurrency systems. ZK-Rollups represent the most visible application, offering169 dramatic improvements in blockchain scalability while preserving security guarantees. Continued research into performance optimization, decentralization mechanisms, and economic incentives will likely determine how widely these technologies are adopted.
As ZK technology matures, we can expect increasing integration with other blockchain innovations, potentially reshaping the cryptocurrency landscape by enabling systems that combine scalability, privacy, and security without the traditional trade-offs that have limited blockchain adoption. The research momentum in this field suggests that Zero-Knowledge proofs will remain at the forefront of cryptocurrency innovation for the foreseeable future.